In the face of a rapidly changing climate and increasing stakeholder pressure, businesses across the globe are reevaluating their practices to align with a more sustainable future.
Nowhere is this shift more apparent than among Forbes Global 2000 (G2000) companies, which are setting the bar by adopting diverse and innovative strategies to decarbonize their operations.
These strategies go beyond traditional measures like energy efficiency and waste reduction to encompass a broader range of transformative approaches, from rethinking supply chains and product design to influencing employee and customer behavior.
Decarbonization Levers
Decarbonization levers refer to specific, actionable strategies that businesses can pull to reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions across their operations, supply chains, and product life cycles. They function like tools in a broader sustainability toolkit, each targeting a unique aspect of a company’s carbon footprint – and companies are using a broader range of these levers than ever before.
By strategically combining and tailoring these levers to their needs, businesses can create comprehensive, high-impact approaches to achieving their decarbonization goals. From optimizing energy use to incentivizing eco-friendly practices among employees and customers, these levers represent a multifaceted approach to addressing the climate crisis while fostering innovation and growth.
Decarbonization isn’t just about compliance with evolving regulations—it’s a business imperative.
Companies that embrace these strategies are not only reducing their environmental impact but also enhancing operational resilience, cutting costs, and strengthening their competitive edge. Publishing transition plans, sustainability reports, and decarbonization roadmaps has become a vital part of corporate transparency, offering valuable insights into how organizations are navigating their low-carbon journeys.
According to Accenture’s “Destination Net Zero” report, which provides a comprehensive analysis of the decarbonization efforts of the world’s 2000 largest companies, levers like Energy Efficiency and Waste Reduction saw only small upticks in adoption, while Materials Sourcing and Employee Incentives rose as “lever leaders”.
Improved communication has done wonders for adoption. More companies are publishing sustainability reports, transition plans, and roadmaps – giving us better insight into the inner workings of corporate decarbonization practices.
This article explores 20 of the most impactful strategies G2000 companies are using to drive decarbonization. Each lever highlights practical, scalable actions businesses can take to lower emissions, mitigate climate risks, and capitalize on opportunities in a carbon-conscious economy.

The full list:
- Energy efficiency
- Waste reduction
- Renewables adoption
- Circular principles
- Buildings
- Working with suppliers
- New products
- Material sourcing
- Employee behavior
- Customer behavior
- Employee incentives
- Fleet decarbonization
- Digital decarbonization
- Offset usage
- Packaging disposal
- Carbon removal
- Travel policy
- Carbon pricing
- Green IT
- Business model change
What do each of these mean, exactly?
Here’s an expanded explanation for each of the 20 strategies for decarbonizing your business, offering a deeper dive into their applications and benefits:
1. Energy Efficiency
Investing in energy-efficient technologies and practices reduces energy consumption and operational costs. Examples include upgrading lighting to LEDs, improving HVAC systems, and optimizing manufacturing processes.
2. Waste Reduction
Implementing waste management systems, such as recycling programs, composting, and waste-to-energy initiatives, minimizes landfill contributions and reduces associated methane emissions.
3. Renewables Adoption
Transitioning to renewable energy sources like solar, wind, or geothermal energy not only cuts Scope 2 emissions but also positions companies as leaders in sustainability.
4. Circular Principles
Adopting circular economy principles means designing products for durability, repairability, and recyclability. It reduces dependency on raw materials and minimizes end-of-life waste.
5. Buildings
Energy-efficient retrofits, green building certifications (e.g., LEED, WELL), and smart building technologies contribute to significant carbon reductions in real estate operations.
6. Working with Suppliers
Partnering with suppliers to improve their sustainability practices, such as adopting low-carbon manufacturing processes, can significantly cut Scope 3 emissions.
7. New Products
Developing innovative, eco-friendly products with a smaller carbon footprint aligns with market demands for sustainability and fosters long-term brand loyalty.
8. Material Sourcing
Opting for sustainable and low-carbon materials—such as recycled metals, bio-based plastics, or sustainably sourced wood—reduces lifecycle emissions from production to disposal.
9. Employee Behavior
Promoting energy-saving habits, such as turning off equipment when not in use or reducing single-use plastics in the workplace, drives cultural shifts toward sustainability.
10. Customer Behavior
Encouraging sustainable consumption through initiatives like carbon labeling, incentives for recycling, or take-back programs empowers consumers to make climate-positive choices.
11. Employee Incentives
Providing incentives for sustainable commuting (e.g., EV subsidies or public transport discounts) or rewards for green practices fosters a motivated, eco-conscious workforce.
12. Fleet Decarbonization
Transitioning to electric vehicles (EVs), hybrid options, or alternative fuels like biodiesel reduces emissions from transportation logistics and corporate fleets.
13. Digital Decarbonization
Optimizing IT infrastructure—like consolidating data centers, switching to energy-efficient servers, and using AI for predictive maintenance—lowers digital energy use.
14. Offset Usage
Purchasing high-quality carbon offsets for unavoidable emissions supports renewable energy projects, reforestation, and carbon sequestration initiatives.
15. Packaging Disposal
Using biodegradable, compostable, or reusable packaging materials addresses waste and reduces the carbon footprint of disposal practices.
16. Carbon Removal
Investing in direct air capture, soil carbon sequestration, or reforestation projects actively removes carbon from the atmosphere to offset emissions.
17. Travel Policy
Implementing sustainable travel policies, such as prioritizing virtual meetings, using rail over air travel, or encouraging ride-sharing, minimizes travel-related emissions.
18. Carbon Pricing
Integrating internal carbon pricing incentivizes departments to adopt low-carbon solutions, while external pricing aligns business strategies with market trends.
19. Green IT
Reducing IT-related emissions through energy-efficient hardware, software optimization, and leveraging sustainable cloud computing practices ensures tech operations align with sustainability goals.
20. Business Model Change
Transforming core business operations, such as shifting from selling products to offering services (e.g., product-as-a-service models), supports long-term sustainability and decarbonization.
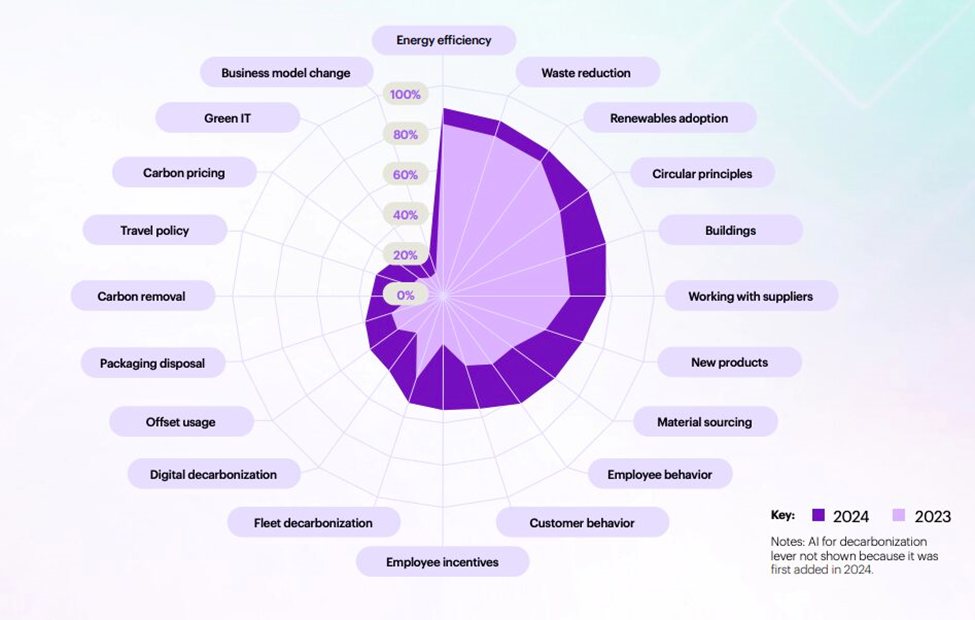
Source: Accenture’s Destination Net Zero Report (link)
Charting the Path to a Low-Carbon Future
These strategies provide a comprehensive roadmap for businesses at any stage of their decarbonization journey, illustrating how each lever contributes to overarching climate goals.
As the urgency of climate action grows, the strategies outlined above demonstrate that decarbonization is both achievable and beneficial for businesses willing to innovate and adapt. By leveraging these 20 approaches, companies can create ripple effects across industries, influencing supply chains, markets, and consumer behavior. The efforts of G2000 leaders illustrate how adopting a multi-faceted approach to sustainability can drive meaningful impact, improve operational efficiencies, and deliver long-term value for stakeholders.
However, decarbonization is not a one-size-fits-all process. Each business must assess its unique challenges and opportunities to create a tailored roadmap. Collaboration, transparency, and a commitment to continuous improvement are essential for achieving net-zero ambitions. Whether you’re retrofitting buildings, rethinking product designs, or empowering your workforce to make greener choices, every action contributes to a collective solution.
The time to act is now. By integrating these strategies into your business model, you not only align with global sustainability goals but also future-proof your organization in an era where climate leadership is a prerequisite for success. Together, we can chart a course toward a more sustainable, resilient, and prosperous future.
